Strategies for Options Trading
Using options, we can make money from the market irrespective of how it is moving, i.e. whether there’s an uptrend, downtrend, or sideways trend.
In this article, we are going to learn about various options trading strategies. Our strategies need to vary as per the market. So, we need to adopt different strategies for bullish, bearish, and neutral markets.
Though many Demat account portals and software provide these strategies as readymade modules, and you are just required to guess the trend in the market. But it’s always a good idea to understand the basics of these strategies – know what is being done exactly and why.
 Note
NoteThis article expects that the readers know the basics of options trading. If you do not, you may read the following articles of ours:
- Article on Futures Vs. Options
- Article on ITM, ATM, OTM
- Article on Option Greeks – delta, gamma, theta, vega, rho.
Moreover, you should know that:
Buying or holding a call or put option is called a long position. Loss of option buyer is limited to the premium paid by him, but he can gain unlimited profit. It’s a bit like lottery ticket, wherein the most you will lose is the amount you paid for the lottery. However, probability of options buyers making a profit is generally lower. Though if you are new to options trading, you should probably start by buying options.
Selling or writing a call or put option is called a short position. Loss of option seller can be unlimited, but his gain can at most be equal to the premium paid by the buyers. However, probability of options sellers making a profit is generally higher. Most of the option sellers are generally professional traders with a lot of experience and deep pockets.
Most of the strategies given in this article will limit the maximum profit you can make (or reduce it to some extent), but will also hedge your position, i.e. chances of you making huge losses will reduce too. Also, in case of most of these strategies, the probability of you making a profit increases (as compared to just simply buying or selling a call/put option, i.e. naked options). So, in the long run these strategies will help you make money from the stock market by helping in your risk management.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents- Options Trading Strategies for Bullish Market
- Options Trading Strategies for Bearish Market
- Options Trading Strategies for Neutral Market
- Strategies for Volatile Market - Straddle & Strangle Option Strategies
- Other Strategies
- Some Miscellaneous Strategies from Trading Experts
- Some Miscellaneous tips regarding Options trading
- Useful Software for Options Trading
Options Trading Strategies for Bullish Market
If the market is bullish (i.e. it’s showcasing an upward trend), or we expect it to be bullish, we may use the following strategies.
Buy Call and/or Sell Put
It’s pretty simple. If we expect the market to be bullish, we buy call options, or sell put options. We can do both too.
This is a very basic concept of options trading – not a genius strategy or something!
Bull Call Spread and Bull Put Spread Strategies
In these two pretty similar strategies, we expect the market to be slightly bullish (so Bull), and we buy the options as well as sell them (hence called Spread).
- In Bull Call Spread strategy, we buy and sell call options (hence the name Call). We buy one ATM (or ITM) call option and sell one OTM call option (i.e. in 1:1 ratio).
- In Bull Put Spread strategy, we buy and sell put options (hence the name Put). We sell one ATM (or ITM) put option and buy one OTM put option (i.e. in 1:1 ratio). Or we can sell one OTM put option and buy one Deep OTM put option.
Cost paid by you = Premium paid in buying the option – Premium received on selling an option
Maximum loss = Cost paid by you × Lot Size
Maximum profit = (Difference in the Strike Prices of the two options - Cost paid by you) × Lot Size
 Note
NoteIn Bull Call Spread strategy, to find the breakeven point in bullish market, i.e. the point above which you will start making profit, just add the cost paid by you in the strike price of the ATM CE option.
Advantages of these strategies are as follows:
- Using these strategies, we hedge our position. When we do so, our loss can no longer be unlimited. Both our loss and profit will have an upper cap. You should take on a trade wherein the maximum possible profit is higher than the maximum possible loss, or if your chance of making profit is high (even if the possible profit is less than the possible loss). It will depend on your risk-reward strategy (Some Demat account portals and software allow you to see all this data.)
- As you are both buying and selling options, the margin requirement decreases. So, you need less capital to do the trade. On the other hand, if you would just have sold the option, the margin requirement would have been higher. That’s because, when you both buy and sell option of the same kind, you are basically hedging your position – your loss is no more unlimited. So, margin requirement will obviously decrease.
- You may make some profit even if the market moves sideways or slightly opposite to what you expected (i.e. even if it was a bit bearish).
- As your maximum loss is limited, you need not watch the market every day. Also, as risk management is inbuilt in the strategy, you need not use stop loss. So, you can stay in the market even if it is moving completely against you – maybe it will reverse at the last moment and earn profits for you. Using this strategy, you may remain in the game till the last moment.
 Note
NoteWe use these strategies when we think that the market will only be slightly bullish. If you think that the market is going to be heavily bullish, there are better strategies out there that may give you even better profits. Also, for these strategies to work better, there should be decent liquidity in the stock you are trading in (liquidity is not an issue in case of indices).
There’s an upper cap on profits in Bull Call Spread and Bull Put Spread Strategies. No matter how much the market rises, you cannot earn more than the maximum possible profit limit. These strategies may not always be that good when seen from the point of view of risk-reward ratio. However, if your view regarding future market movement is correct, you will make profits.
Moreover, note that risk-reward ratio of bull call spread is better than that of bull put spread. But probability of making a profit is better in bull put spread, than in bull call spread. In bull call spread you will have to give out some money the very first day (i.e. there is net premium outflow – you will kind of be in the category of option buyers) and so you will be in a loss-making position the very first day, and will have to wait for your position to become profitable (with low probability of making a profit just like option buyers). So, many experts prefer bull put spread over bull call spread.
Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy
We use this strategy if we expect the market to be highly or at least decently bullish.
Herein we buy and sell call options, but not in 1:1 ratio. We do it in some other ratio (that’s why called Ratio Spread).
In this strategy, we sell one ATM call option, and buy two OTM call options (1:2 ratio).
Advantages of this strategy are as follows:
- Using this strategy, we hedge our position. When we do so, our loss can no longer be unlimited. Though our profit can still be unlimited.
- As you are both buying and selling options (i.e. you are hedging), the margin requirement decreases. So, you need less capital to do the trade.
- You may make some profit even if the market moves opposite to what you expected (i.e. even if it was bearish). But in such a case the profit will not be unlimited – you will make a limited amount of profit.
 Note
NoteBull Call Spread and Bull Put Spread Strategies are used when we expect the market to be slightly bullish. If it happens, you will make limited amount of profit. However, you may even make slight profit even if the market moves sideways or slightly downwards.
Now, compare this with Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy.
Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy is used when we expect the market to be a lot bullish. If it happens, you will make unlimited amount of profit. You may make limited amount of profit even if the market moves downwards. However, if the market moves sideways or slightly upwards, you will book loss (even that will be limited). Risk-Reward ratio of this strategy is pretty good.
Options Trading Strategies for Bearish Market
If the market is bearish (i.e. it’s showcasing a downward trend), or we expect it to be bearish, we may use the following strategies.
Buy Put and/or Sell Call
It’s pretty simple. If we expect the market to be bearish, we buy put options, or sell call options. We can do both too.
This is a very basic concept of options trading – not a genius strategy or something!
Bear Put Spread and Bear Call Spread Strategies
In these two pretty similar strategies, we expect the market to be slightly bearish (so Bear), and we buy the options as well as sell them (hence called Spread).
- In Bear Call Spread strategy, we buy and sell call options (hence the name Call). We sell one ATM (or ITM) call option and buy one OTM call option (i.e. in 1:1 ratio). Or we can sell one OTM call option and buy one Deep OTM call option. This is opposite to what we do in Bull Call Spread Strategy.
- In Bear Put Spread strategy, we buy and sell put options (hence the name Put). We buy one ATM (or ITM) put option and sell one OTM put option (i.e. in 1:1 ratio). This is opposite to what we do in Bull Put Spread Strategy.
Cost paid by you = Premium paid in buying the option – Premium received on selling an option
Maximum loss = Cost paid by you × Lot Size
Maximum profit = (Difference in the Strike Prices of the two options - Cost paid by you) × Lot Size
 Note
NoteAs per some experts, Bear Put Spread is a bit more profitable than Bear Call Spread.
In Bear Put Spread strategy, to find the breakeven point in bearish market, i.e. the point below which you will start making profit, just subtract the cost paid by you from the strike price of the ATM PE option.
Advantages of these strategies are as follows:
- Using these strategies, we hedge our position. When we do so, our loss can no longer be unlimited. Both our loss and profit will have an upper cap. You should take on a trade wherein the maximum possible profit is higher than the maximum possible loss, or if your chance of making profit is high (even if the possible profit is less than the possible loss). It will depend on your risk-reward strategy (Some Demat account portals and software allow you to see all this data.)
- As you are both buying and selling options, the margin requirement decreases. So, you need less capital to do the trade. On the other hand, if you would just have sold the option, the margin requirement would have been higher. That’s because, when you both buy and sell option of the same kind, you are basically hedging your position – your loss is no more unlimited. So, margin requirement will obviously decrease.
- You may make some profit even if the market moves sideways or slightly opposite to what you expected (i.e. even if it was a bit bullish).
- As your maximum loss is limited, you need not watch the market every day. Also, as risk management is inbuilt in the strategy, you need not use stop loss. So, you can stay in the market even if it is moving completely against you – maybe it will reverse at the last moment and earn profits for you. Using this strategy, you may remain in the game till the last moment.
 Note
NoteWe use these strategies when we think that the market will only be slightly bearish. If you think that the market is going to be heavily bearish, there are better strategies out there that may give you even better profits. Also, for these strategies to work better, there should be decent liquidity in the stock you are trading in (liquidity is not an issue in case of indices).
There’s an upper cap on profits in Bear Call Spread and Bear Put Spread Strategies. No matter how much the market falls, you cannot earn more than the maximum possible profit limit. These strategies may not always be that good when seen from the point of view of risk-reward ratio. However, if your view regarding future market movement is correct, you will make profits.
Moreover, note that risk-reward ratio of bear put spread is better than that of bear call spread. But probability of making a profit is better in bear call spread, than in bear put spread. In bear put spread you will have to give out some money the very first day (i.e. there is net premium outflow – you will kind of be in the category of option buyers) and so you will be in a loss-making position the very first day, and will have to wait for your position to become profitable (with low probability of making a profit just like option buyers). So, many experts prefer bear call spread over bear put spread.
Put Ratio Back Spread
We use this strategy if we expect the market to be highly or at least decently bearish.
Herein we buy and sell put options, but not in 1:1 ratio. We do it in some other ratio (that’s why called Ratio Spread).
In this strategy, we sell one ATM put option, and buy two OTM put options (1:2 ratio).
Advantages of this strategy are as follows:
- Using this strategy, we hedge our position. When we do so, our loss can no longer be unlimited. Though our profit can still be unlimited.
- As you are both buying and selling options (i.e. you are hedging), the margin requirement decreases. So, you need less capital to do the trade.
- You may make some profit even if the market moves opposite to what you expected (i.e. even if it was bullish). But in such a case the profit will not be unlimited – you will make a limited amount of profit.
 Note
NoteBear Call Spread and Bear Put Spread Strategies are used when we expect the market to be slightly bearish. If it happens, you will make limited amount of profit. However, you may even make slight profit even if the market moves sideways or slightly upwards.
Now, compare this with Put Ratio Back Spread Strategy.
Put Ratio Back Spread Strategy is used when we expect the market to be a lot bearish. If it happens, you will make unlimited amount of profit. You may make limited amount of profit even if the market moves upwards. However, if the market moves sideways or slightly downwards, you will book loss (even that will be limited). Risk-Reward ratio of this strategy is pretty good.
Options Trading Strategies for Neutral Market
If the market is moving sideways (i.e. it’s showcasing a neutral trend), or we expect it to move sideways, we may use the following strategies.
Short Straddle and Short Strangle Strategies
- Short Straddle Strategy: If you expect that the market will move sideways, then we can sell both put (PE) and call (CE) ATM options.
- Short Strangle Strategy: If you expect that the market will move sideways, then we can sell both put (PE) and call (CE) OTM options.
You will make a profit if the market does not rise or fall too much, i.e. if it moves within a range. The theta decay of premium will work in your favour, i.e. option sellers make profit due to theta decay.
So, initially in the trade you may be in the red, but as the time passes you will get in the green zone (i.e. profitable zone). More is the time that passes, more will be the profit that you will make (you may hold your position overnight too). However, the profit you make using these strategies is limited.
On the other hand, if the market moves up or down a lot then you will book loss. In fact, your loss may be unlimited. So, risk-reward ratio in these strategies is not that good.
Also, the margin requirement in these strategies is high. That’s because we are selling options here.
Maximum loss = Unlimited
Maximum profit = Sum of the premiums of the two options × Lot Size
 Note
NoteIn Short Straddle Strategy, you will be in the profit zone if the price moves within the following range:
(ATM strike price - Sum of the premiums of the two options) to (ATM strike price + Sum of the premiums of the two options)
Though the amount of profit you make using this strategy is limited, the probability of making a profit is high.
 Note
NoteIf you want to be even more sure to make profit in Short Strangle Strategy, you may also sell Deep OTM options, though your maximum profit will reduce a bit.
 Note
NoteIn both Short Straddle Strategy and Short Strangle Strategy, the possible profit is limited. Though in Short Straddle Strategy the maximum possible profit is a bit higher than the maximum possible profit in Short Strangle Strategy. Though in both the strategies you may incur unlimited losses.
Also note that, while in Short Straddle Strategy the range in which you will make a profit is small, in Short Strangle Strategy this range is larger. So, even if there are more price fluctuations in the sideways market, Short Strangle Strategy may still make you profit - though the maximum possible profit will be less.
Short Iron Butterfly Strategy
Just like the Short Straddle Strategy given above, even here we sell both put (PE) and call (CE) ATM options. However, here we do something extra to be safer.
In this strategy, we hedge our position by buying an OTM call option and an OTM put option. OTM options have a low premium, so you won’t have to spend much to do this hedging.
But make sure that you buy the OTM options before you sell the ATM options. This will reduce the margin requirement needed for selling the ATM options.
Net Premium Received = Sum of the premiums received from the two ATM options - Sum of the premiums paid for the two OTM options
Maximum profit = Net Premium Received × Lot Size
Maximum loss = {Difference in the strike prices of ATM options sold and OTM options bought - Net Premium Received) × Lot Size
 Note
NoteShort Iron Butterfly Strategy is better than Short Straddle and Short Strangle Strategies. That’s because in Iron Butterfly Strategy your loss is limited (while in other two strategies the loss may be unlimited). That’s why here the risk-reward ratio is good. You may earn even 4-5 times the risk you are taking.
Also, the margin requirement reduces in Short Iron Butterfly Strategy. That’s because we are not only selling, but also buying options to hedge our position.
Short Iron Butterfly Strategy is an expiry special strategy, i.e. it will work better on the expiry day.
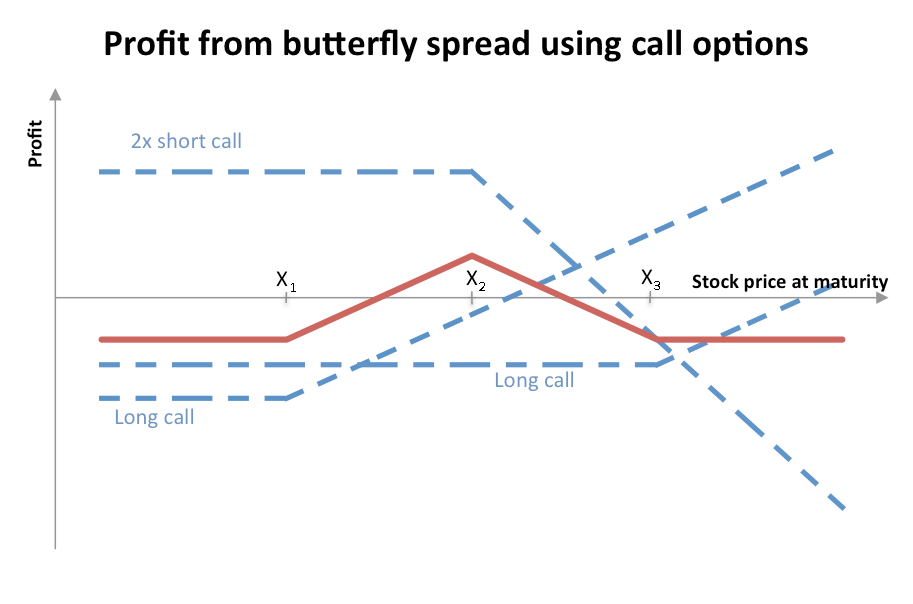
 Note
NoteIn Butterfly Strategy (not Iron Butterfly Strategy), we sell two ATM call options. We also buy one ITM call option, and one OTM call option. You may buy more lots too, but the ratio should be the same. Risk-reward ratio of Iron Butterfly Strategy is better than Butterfly Strategy.
 Note
NoteWhile Short Iron Butterfly Strategy is used when we expect the market to be neutral, we use Long Iron Butterfly Strategy when we expect the market to be volatile, i.e. when we expect a sharp move either up or down in the underlying stock during the life of the options.
Short Iron Condor Strategy
We use this strategy when our outlook is neutral on direction but bearish on volatility (rising volatility reduces the profit, as premiums rise with increased volatility). In other words, we expect the volatility to reduce once the position has been initiated.
Here we have to:
Sell two options - Lower Middle Strike Put and Higher Middle Strike Call.
Buy two options - Lower Strike Put and Higher Strike Call. That is, the long put’s strike price is lower than the long call’s strike price. Or in other words, this strategy involves a bear call spread (selling Higher Middle Strike Call and buying Higher Strike Call – generally OTM calls), and a bull put spread (selling Lower Middle Strike Put and buying Lower Strike Put – generally OTM puts).
All the options traded in this strategy belong to the same underlying asset and have the same expiration date.The risk-reward ratio of this strategy is good.
Time decay would benefit the trader, as long as the position is profitable.
Maximum possible loss is limited.
We use this strategy when we expect the underlying asset to remain in a range and consolidate near the two middle strikes
Net Premium Received = Sum of the premiums received - Sum of the premiums paid
Maximum profit = Net Premium Received × Lot Size
Maximum loss = {Difference in the strike prices of the bull put spread or bear call spread - Net Premium Received) × Lot Size = {Lower-middle strike price - Lower strike price - Net Premium Received) × Lot Size
 Breakeven stock price at expiration
Breakeven stock price at expirationIn this strategy, we get two breakeven points:
The lower breakeven point = Lower Middle strike price of the short put - the net premium received.
The upper breakeven point = Higher Middle strike price of the short call + the net premium received.
Strategies for Volatile Market - Straddle & Strangle Option Strategies
If there’s a lot of volatility in the market, i.e. IV is high, then it means that there will be no sustainable trend in the market. It will swing up and down.
In such a market (or if we expect the market to be such) we can use Straddle & Strangle Option Strategies to make profits. However, they are not very reliable.
In fact, as per some experts they are the closest that options trading can come to gambling and lottery. That’s because the maximum loss you may incur is the capital (i.e. premium) you invested (akin to the cost of a lottery ticket). But if these strategies work, you may book huge profits (even by investing very less capital, just like a lottery).
Long Straddle Strategy
If you expect that the market will move a lot upward or downward (i.e. it will be a lot volatile), then we can buy both put (PE) and call (CE) ATM options.
Maximum profit = Unlimited
Maximum loss = Sum of the premiums paid for the two ATM options × Lot Size
 Note
NoteIn Short Straddle Strategy, we sell the options. Here we buy the options. Short means selling, and Long means buying. Straddle means you are dealing with ATM options.
Long Straddle Strategy is not an appropriate strategy for the expiry day, or near the expiry day. So, avoid it on Thursdays and Wednesdays.
Long Strangle Strategy
If you expect that the market will move a lot upward or downward (i.e. it will be a lot volatile), then we can buy both put (PE) and call (CE) OTM options.
Here you will have to pay a bit less premium than in long straddle strategy, as here you are buying OTM options and not ATM options. So, it’s even more “lottery-like” as compared to the Long Straddle Strategy.
 Note
NoteIn Short Strangle Strategy, we sell the options. Here we buy the options. When we sell options (i.e. acquire short position), theta works in our favour and so we may hold our positions over multiple days. However, when we buy options (i.e. acquire long position), we should complete the trade as soon as possible, preferably do intra-day trade.
Some common tips for Long Straddle and Long Strangle Strategies: Both of these strategies are pretty similar, with some minute differences. Both of them are executed when we have a similar view of the market – that it will be volatile. Further, there are a few tips that will come handy in both of these strategies:
- You have to make sure that both the trades (call and put) are executed at the same time. For this purpose, you may create a basket in your Demat account (if that feature is available), and put in it the options that you want to buy. Then buy them at the same time.
- As in this strategy we buy options, theta decay comes into play. If you will buy these options on Wednesday or Thursday, you will see that premium decays much faster than it did on say Friday, Monday, Tuesday. Whenever your option strategy involves theta decay, i.e. if theta is working against you (like in these strategies), it is better to do intra-day option trade – start and execute the trade the same day.
- If market shows some volatility (i.e. your view was right and the market moves up or down a lot), then you will make profit using these strategies. However, if the market moves sideways (or shows very little uptrend/downtrend), then theta decay will become more predominant and will eat up your premium, i.e. you will book loss.
- If the market moves up or down a lot, then you will lose your premium in either the call or the put option. But the one of them will make you huge profits. To be precise, you will make profits if the market moves a lot, more than the premium you paid. Hope you get the logic behind these strategies. When we buy options, our loss is limited to our premium, but we can make unlimited profits. So, here our risk = premium, and reward = unlimited.
- While using these strategies, you need not use stop loss. That’s because buying both call and put options is kind of a risk management in itself. The only way you may lose money using these strategies is through theta decay of the premium.
- In these strategies, the probability of you making a profit is comparatively less. That’s because these strategies require the market to move a lot (either rise a lot, or fall a lot), but we know that generally the markets/indices/stocks do not move so much in a short period of time. You may witness such huge movement in markets on some special days or events, such as election result day, budget announcement day, etc.
Other Strategies
Let’s have a look at some other well-known strategies.
Call Ratio Spread Strategy
In this strategy, we:
- buy one ATM or OTM call option.
- sell two OTM (higher strike) call options.
 Note
NoteCall Ratio Spread Strategy is different from Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy that we studied earlier. Don’t get confused.
Put Ratio Spread Strategy
In this strategy, we:
- buy one ATM or OTM put option.
- sell two OTM (lower strike) put options.
 Note
NotePut Ratio Spread Strategy is different from Put Ratio Back Spread Strategy that we studied earlier. Don’t get confused.
Long Iron Condor Strategy
We use this strategy when our outlook is neutral on direction but bullish on volatility, i.e. rising volatility enhances the profit. So, once we have initiated a position we expect the volatility to increase.
Here we have to:
- Buy two options - Lower Middle Strike Put and Higher Middle Strike Call.
- Sell two options - Lower Strike Put and Higher Strike Call. That is, the short put’s strike price is lower than the short call’s strike price.
Or in other words, this strategy involves a bear call spread (buying Higher Middle Strike Call and selling Higher Strike Call – generally OTM calls), and a bull put spread (buying Lower Middle Strike Put and selling Lower Strike Put – generally OTM puts).
All the options traded in this strategy belong to the same underlying asset and have the same expiration date.
- The risk-reward ratio of this strategy is not that good.
- Time decay would hurt the trader.
- Maximum possible loss is limited.
Net Premium Received = Sum of the premiums received - Sum of the premiums paid
Maximum profit = (Lower-middle strike price - Lower strike price - net premium paid) × Lot Size
Maximum loss = Net Premium Received × Lot Size
 Breakeven stock price at expiration
Breakeven stock price at expirationIn this strategy, we get two breakeven points:
- The lower breakeven point = Lower Middle Strike Price - Net Premium Paid.
- The upper breakeven point = Higher Middle Strike Price + Net Premium Paid.
 Note
NoteRegular Condor spread involves only calls or only puts. While, Iron Condor strategies (both Short and Long) involve both calls and puts.
- Regular Condor spread strategy is an extension of Butterfly spread strategy.
- Iron Condor spread strategy is an extension of Iron Butterfly spread strategy.
 Note
NoteDo not start applying these strategies in live market with your hard-earned money just like that. Before trading in live market, you must paper trade. That is, use some dummy software that replicates the stock market, or just use a paper/excel, and then see whether your strategy worked, check your accuracy. Practice before you play the real match!
Also, it’s suggested for beginners that they should start doing options trading in Nifty and Bank Nifty. That’s because on these indices all these strategies work better, and margin requirements are lower too. However, Bank Nifty is a lot more volatile than Nifty. So, to be doubly safe, start with Nifty. Though Nifty has a bigger lot size than Bank Nifty.
Some Miscellaneous Strategies from Trading Experts
Strategy 1: Use PCR ratio and VWAP
In this strategy, we trade based on data, not on price action. That is, we do not look at candlestick or chart patterns. Rather we rely on data and some indicators. This strategy is mainly based on two sets of data: PCR ratio and VWAP.
Put-Call ratio, P/C ratio, or PCR: It is the ratio of change in put open interest options and change in call open interest options. In simple words, it is the ratio of the amount of put strikes bought to call strikes bought in that day (so relevant for intra-day traders that aim to buy options).
- If more people think that the price of the underlying asset will move up, then more people will buy call option rather than put option. So, PCR will be below 1.
- If more people think that the price of the underlying asset will move down, then more people will buy put option rather than call option. So, PCR will be above 1.
However, share market is commanded and given direction by the big bulls, i.e. the bigger players. When it comes to option buyers and option sellers, the later ones are the bigger players. That is, generally the price of the underlying asset will move as the sellers will like it to move, as they have deep pockets. That’s why around 90% of the option buyers make losses, while option sellers generally make profits more often.
So, if option sellers see that:
- more people are buying call option (i.e. they are anticipating an uptrend), they will bring down the price of the underlying asset.
- more people are buying put option (i.e. they are anticipating a downtrend), they will bring up the price of the underlying asset.
Aim of option sellers is to gain at the cost of option buyers by taking away their premiums. If you have this knowledge, you can make use of it to make profits and predict the price action to a large extent. In share market, we try to swim with the big fishes.
So, this is what you need to do as an option buyer:
- If you see that PCR is way below 1 (ideally below 0.75), then it means that most option buyers are buying call options and so anticipating the price to rise. Now, what do you think the option sellers will do? – Obviously, they will try to do the opposite and bring down the price. More often than not they will succeed. So, if you see PCR way below 1, buy put option.
- If you see that PCR is way above 1 (ideally above 1.25), then it means that most option buyers are buying put options and so anticipating the price to fall. Now, what do you think the option sellers will do? – Obviously, they will try to do the opposite and bring up the price. More often than not they will succeed. So, if you see PCR way above 1, buy call option.
- PCR between 0.75 and 1.25 is a pre-indication of sideways price movement.
 Note
NotePCR ratio is based on “Change in Open Interest”, which is the options traded on that particular day. So, here real money is involved. That’s why Change in Open Interest is such a strong indicator – it is a precursor (or pre-indicator, or leading indicator) to the price action of the market, i.e. market will move as per it.
On the other hand, many other indicators used by traders (e.g. moving averages, etc.) make use of the price movement of the market; they are based on how the market moves. That is, they are follow-on indicators, or lagging indicators.
 Note
NoteStart at around 11 AM – 12 noon, and then try to predict the trend of the market, i.e. whether it will go up or down. PCR ratio keeps getting more accurate with time. As per some experts, it’s the most accurate around 1 to 2 PM. As far as the days are concerned, the accuracy is the best on Wednesdays.
This PCR data is generally based on change in open interest. So, it’s more relevant for Intra-day traders. Moreover, PCR data is more useful for option buyers, but sellers may also use it to a certain extent. Though we can also calculate PCR ratio based on total outstanding open interest – this is more useful if you want to know the overall weekly trend (but as most option buyers do intraday trading only, it’s not that useful for them).
Also keep in mind that the PCR ratio may change midway at any time. So, keep on looking at this ratio every 5 to 15 minutes. Have a look at PCR slope, which represents the trend of PCR data – whether it’s increasing or decreasing. Remain updated! Change your strategy accordingly, or else you will end up making losses. As per some experts, the slope of PCR is even more significant than the absolute value of PCR.
In fact, there are some software that even provide us the PCR data in chart format, and we can technically analyse this PCR chart just as we do in case of stock price charts.
Also, keep in mind that often PCR shows a lot of change (and fast change) between 1:30 PM and 2:30 PM. Be vigilant at this time. Whatever trend is visible in PCR will most probably soon be reflected in the price of the underlying asset.
Apart from using the PCR data, you should also make use of the signals given by VWAP line.
VWAP: VWAP stands for Volume-Weighted Average Price. It gives us an indication regarding the mean price of the market. In other words, it indicates the price at which most of the volume of the market is concentrated. It’s an indicator that we can use in most of the broker apps.
 Note
NoteFor the sake of options trading, you should apply this VWAP indicator on the futures chart of the index/stock, and not on its simple index/stock chart. For example, you should apply it on NIFTY FUT chart, and not on NIFTY chart. So, the VWAP price we are talking about is that of the futures, and not that of the underlying asset. Even if you are trading in options, you will consider this only.
VWAP also gives us an indication of the trend of the market. If stock price tends to stay above the VWAP, it indicates that the market is bullish (big players are not letting the price to fall below the VWAP line). On the other hand, if stock price tends to stay below the VWAP, it indicates that the market is bearish (big players are not letting the price to rise above the VWAP line).
So, if both PCR data and VWAP indicate the same trend, you may think about trading in that direction. Let’s consider some scenarios:
- PCR > 1.25, and it’s increasing further, and stock price is above the VWAP: It means that the market is bullish. Buy share, or buy call option, or sell put option.
- PCR < 0.75, and it’s decreasing further, and stock price is below the VWAP: It means that the market is bearish. Sell share, or buy put option, or sell call option.
However, if these three data points contradict each other, you may skip the trade to be on the safe side. If you still want to trade, make sure at least two of them are on your side. We give the most importance to PCR slope (i.e. how PCR is changing per 5 minutes or so), then to the absolute value of PCR, and the least to VWAP. Again, let’s consider some scenarios.
- PCR > 1.25, and it’s increasing further (i.e. PCR has an upward slope), but stock price is a little below the VWAP: It means that the market is bullish. You may buy share, or buy call option, or sell put option. We give more importance to PCR data than VWAP, as far as predicting trend is concerned.
- PCR < 0.75, and it’s decreasing further (i.e. PCR has a downward slope), but stock price is a little above the VWAP: It means that the market is bearish. You may sell share, or buy put option, or sell call option.
- PCR is around 1 (a little below or above it), but it’s increasing further, and stock price is also above the VWAP: It means that the market is probably getting bullish. You may buy share, or buy call option, or sell put option.
- PCR is around 1 (a little below or above it), but it’s decreasing further, and stock price is also below the VWAP: It means that the market is probably getting bearish. You may sell share, or buy put option, or sell call option.
So, now we know the upcoming trend. But when to enter the trade? – Here also VWAP comes handy.
While PCR data gives you an indication of the direction in which the price of the underlying asset will move, it does not tell you about the right entry and exit points, i.e. when to enter/exit the trade. Here, VWAP comes into play.
As per some experts, we should enter when the price approaches near the VWAP line, i.e. at or near a point where the price of the underlying asset is touching the VWAP line. If we do so, we will in a position to book the maximum profits.
You should exit the trade when the price is further away from the VWAP line and is about to reverse its direction and move again towards the VWAP line. For this, you may take help of technical analysis that will help you find the pervading resistance and support levels in the market.
Entering near the VWAP line also allows us to keep a small stop loss (though some option buyers do not use a stop loss and are ready to sacrifice their premium), as the chances of the price to break VWAP by a large margin are minimal.
 Note
NoteYou may set the VWAP to change per tick, or you may also use 5 minute or 15 minute VWAP. VWAP value does not vary/change that much based on the time period – you may use any.
 Note
NoteEven if the market opens at a very high or low level as compared to VWAP, it will generally touch VWAP at least once in the day. In general, market price tends to touch the VWAP price a few times in a day. That’s supposed to be the right entry point for traders. If it does not, you may skip trading that day.
As per some experts, entering the trade at breakout/breakdown is not that good a strategy for options trading (though in cash based intraday trading we often do this). Option traders should rather try to enter the trade near the VWAP line.
 Note
NoteTo see both PCR ratio and VWAP signal, you could use various software and websites, such as Autotrender.
Strategy 2: Strategy based on Expiry
Some traders buy index options on the expiry day, which is Thursday for options. That’s because premiums decrease a lot by Thursday due to theta decay, and so it’s cheaper to buy options. So, even small retailers with limited amount of capital can trade on the expiry day – they can buy even ATM and ITM options at a pretty reasonable rate.
Also, if your view is right, you may get a lot of price jump (i.e. movement) on Thursday. But risk is also higher on the expiry day.
You need more expertise on the expiry day when it comes to placing the appropriate stop loss. That’s because premiums are a lot less on the expiry day, and theta decay further complicates this issue.
Vishal Mehta, an expert algo trader, does option selling only on Wednesdays and Thursdays, as here the rate of theta decay is the fastest, and so chances of option sellers booking a profit are the most. As per him, Super Trend is a good indicator for options sellers.
However, trading on stock options on the expiry day is very risky, especially after 1 PM (for both option buyers and sellers).
 Note
NoteThough index options (e.g. NIFTY options) have a weekly expiry, stock options have a monthly expiry. Monthly expiries are a lot more volatile than weekly expiries. That’s because there are a lot of positions, and traps (bull trap, bear trap, etc.) here.
Strategy 3: Call Cover or Covered Call Strategy (Options as Insurance)
You may also buy or sell options as an insurance cover, i.e. to hedge your positional trade. For example, if you expect the market to go up and have bought some shares for positional or swing trading, you may also buy OTM PE options as an insurance. If the market goes down, this OTM PE option will cut your losses.
Or else, you may sell OTM CE option. Say, you expect a stock to go from 2500 to 2600, and have bought the stock at Rs. 2500 (spot price). But to cover your losses you may sell an OTM CE option (i.e. call option) having a strike price of 2600. If the price moves down (instead of moving up), it will cut some of your losses. Also, if the stock rises slowly from 2500 to 2600, you will still earn through time decay of the premium paid by the option buyers. So, by the time the price reaches 2600, not only will you profit due to the price rise of the stock, but also by earning the premium till the time it does not reach 2600.
While using this strategy, and if you are selling OTM CE option, we should have a look at the resistance level of the underlying asset too. We should not use this strategy if the stock is near its resistance level (in this case, the chances of a breakout happening may increase). If the stock price is well below the resistance level, we can safely adopt this strategy.
Strategy 4: Put Selling Strategy
Sometimes we tend to wait for the price of a stock or index to fall to a certain level before we buy it. But using Put Selling Strategy we can earn profits while we are waiting for the price to fall down.
Say, we want to buy a stock at Rs. 2400, but at present it’s trading at Rs. 2500. So, we can sell an OTM PE option (i.e. put option) having a strike price of 2400. Till the price of the stock is above 2400, you will earn profits through premium decay of option buyers. Once the price hits your desired level of 2400, you can buy your stock and sell the option.
Some Miscellaneous tips regarding Options trading
Now, after we have seen a number of strategies for options trading, let’s list down some general dos and don’ts in this regard.
Buy ATM options
New option traders should start with buying options, rather than selling them. Risk in option buying is limited, and margin requirement is low too.
Moreover, newbies should prefer to buy ATM options. Avoid OTM options. Though premium of OTM options is very low, chances of you booking losses here are much higher because of theta decay.
Though you may also trade in slightly ITM options.
 Note
NoteAs per some experts, in intra-day trading you should choose ATM or ITM options having delta between 0.4 and 0.6.
Develop Specialization
Rather then trading in multiple indices and stocks, you should trade in a limited number of them. This way you will develop some specialization in those areas, get acquainted with the price action, how the operator works, etc. Naturally, your accuracy will improve.
For example, we trade just in Nifty, Bank Nifty and a handful of 6-7 big stocks.
Keep Learning, Analysing and Researching
Apart from this, keep on paper trading, and practicing. Try out the accuracies of various strategies, indicators, software, etc. Do a lot of back data research.
Also, maintain a diary or excel sheet wherein you should write the reasons behind success or failure of your trade. Do this every day after you are done trading.
Risk Management
Always do reward-loss ratio analysis. That is, decide how much loss you are willing to take before you start trading. Use Stop loss order with Trigger levels accordingly.
On non-expiry days, you may keep your stop loss at 30-40% of your premium. On the expiry day, you may keep the stop loss at 50% of your premium. That’s because premiums are nevertheless a lot low on the expiry day anyways.
The risk-reward ratio should generally be better than 1:1.5. That is, you should enter a trade only if you think that for 1 unit loss, you stand to gain a profit of at least 1.5 units or more. Novice traders often keep their stop loss big and their targets small – they book profits as soon as they can (maybe because they are a bit underconfident and nervous). In the long run, they tend to accumulate a series of small profits and big losses. Entering near VWAP will improve this ratio for you.
As per some experts, we should keep the stop loss around 10 points below the day low (if you are buying call), or above the day high (if you are buying put). That’s because during stop loss hunting the price often touches the day low/high. So, we should keep our stop loss a bit below/above it. But make sure that the stop loss is not too wide/big, or else our risk-reward ratio will not be good.
You may also use Standard Deviation (SD) for setting stop loss and target. If you enter the trade near the VWAP line (i.e. near the mean price), you may keep the stop loss as 1.5 to 2 times of the Standard Deviation, and the target as 2.5 to 3.5 times of the Standard Deviation. Say the mean price is 100 and SD is 10 – then in a bullish market you can buy a call option by putting the stop loss at 80 to 85, and set a target of 125 to 130. You may book 50% of the profit once your target reaches 2 to 2.5 times of the Standard Deviation, and apply a trailing stop loss for the rest.
 Note
NoteIf Standard Deviation (SD) is high, it may be a reflection of a volatile market, i.e. there may be much uptrend/downtrend in the market. It is a good opportunity for option buyers.
If Standard Deviation (SD) is low, it may be a reflection of a non-volatile market, i.e. there may be a sideways movement in the market. It is a good opportunity for option writers/sellers, as in a sideways market option sellers earn through time decay of the premiums.
Though low volatility also means low premiums. Keep that in mind. If you sell options for a longer time-frame (say a month), while the volatility is low, you might be running a risk. If the volatility rises during the month, the premiums will rise too and it may nullify the effect of time decay of premiums. That’s why some option sellers do not sell monthly options if India VIX is below 20.
As a thumb rule, as soon as you see that you are making a loss of more than Rs. 1500 in naked options (per lot), or a loss of more than Rs. 1000 in spreads (per lot), then you should exit instantly. Such a huge loss means that your view/expectation was wrong. If you wait any further, you may suffer severe losses. Now your only priority should be to cut your losses. You may apply your stop losses accordingly to automate this process.
 Note
NoteRemember that risk-reward ratio is even more important than accuracy. This is how you become profitable in the long run.
You may make use of trailing stop loss too – it will help you maximize profits. It’s more important than you think. As per some experts, you may aim for 20 to 50 points profit per lot. Once you have attained 20 points of profit, and you think that you may earn a lot more, you may apply a trailing stop loss by placing it initially at the cost of the premium paid by you (or maybe more, as you deem fit).
Position Size
Also, your position size should be decent. Don’t try to make big trades with limited amount of capital (i.e. do not over-leverage). If you do so, you may lose all your capital even if you hit the stop loss once.
To give you some idea of the decent position size, you:
- should not trade more than 1 lot, if you have a capital of 1 lakh rupees.
- should not trade more than 5 lots, if you have a capital of 5 lakh rupees.
After that, you may increase your position size by 50% per 5 lakh rupees of capital. So, if you have 10 lakh rupees, you may trade 5 + 50% of 5 = 5 + 2.5 = 7.5 lots (i.e. 7 or 8 lots)
Hope, you get the idea. If you want to play it a bit riskier, you may trade 1 lot per 50 thousand rupees of capital too.
Book profits in a step-wise manner
If you can book profit in between, book it. Need not wait for the market to reach your intended target.
For example, you may sell 50% of the options, so as to ensure that even if the rest of the options hit SL (Stop Loss), you will not be in a loss overall. Conserving your capital should be your first priority in share market.
Avoid Overtrading and Greed
Do not over trade, i.e. do not be too greedy. Book profits as soon as you reach a decent level.
New traders should avoid carrying their positions overnight (i.e. to the next day), especially if they are trading in naked options. Newbies often carry their position overnight if they are in loss, thinking that things may get better the next day. But this may also lead them to losing all their capital (i.e. premium). They should book profit/loss the same day, and start afresh the next day.
 Note
NoteOption sellers/buyers may carry forward their position to next day only if they are hedged, e.g. in spreads. Don’t do this if you have bought/sold naked options. However, option buyers may lose a lot of premium due to overnight theta decay. Keep that in mind!
However, some people take this advice to an extreme level and do scalping, i.e. they book small profits to be in the safe zone and avoid losses at any cost. Their strategy is to make a lot of small profits and avoid losses, rather than making big profits. For this purpose, scalpers may undertake even 10-15 trades in a day. Though there’ nothing wrong in it. However, some experts suggest that we should rather wait for 3-4 good opportunities for trading, and aim for a bit bigger profit (but don’t be too greedy).
Also, make sure to increase your trading amount gradually. Say if you make profit in the first trade, and then in the second trade you increase the capital. Let’s assume that you make profit again, and then again increase your capital for the third trade, and so on. Essentially, you are getting greedy and increasing the bets every time. If you make a loss any time, it may nullify all the profits made earlier. Never put yourself in that position.
As a rule of thumb, trade equal lots/capital for some time (say a month, or till you earn enough profits). Thereafter, you may increase the trade capital or lot size. Now, trade with that amount for a certain period before you increase it again. And so on.
Avoid Sideways Trend
Do not invest in sideways market - it’s called NTZ (No Trading Zone) by some experts.
That’s because, if you do so, you will have to wait a long time and that will lead to premium decay. An option’s premium decay accelerates as the expiration date gets closer, because there’s less time for an investor to earn a profit from the option. Theta (one of the many option Greeks) measures the rate at which the option premium declines due to time decay.
 Warning
WarningDo not hold naked index weekly expiry options for more than two days at any cost. Otherwise, theta decay will almost completely erode your premium.
Useful Software for Options Trading
- Upstox Calculator: You may use it to find the margin you need to trade using any strategy.
- Zerodha F&O margin calculator
- Sensibull
- Opstra
 Note
NoteIndex options such as that of Nifty and Bank Nifty have a weekly expiry. Whereas, stock options have a monthly expiry.
Bank Nifty shows faster up and down trends as compared to Nifty, i.e. faster movement. So, if you are looking for a hero-zero option trade, you should do it in Bank Nifty. Hero-Zero trade means that either you will lose a lot or gain a lot.
 Note
NoteOptions Trading is a Zero-Sum game. For some to make profits, others must suffer losses.
 Note
NoteFor most of the above strategies to work, you should have a fair idea of how the market is about to move in future, i.e. the price action. To know this, traders do technical analysis. If you want to learn this craft, you may read these articles of ours: